Lesion Characteristics
Lesion Size (diameter): 8mm
Lesion Location: Left Upper Lobe (LUL) pleura-based, solid lesion
Visible on Fluoro: No
REBUS Verification: No
Case Details
Procedure Time: 30 Minutes for bronchoscopy procedure
Final Pathology Report: Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Patient Background
A 70-year-old female patient with no smoking history but a history of head and neck cancer presented with an 8mm LUL nodule and an enlarged hilar lymph node.
The Procedure
Planning
To begin planning of the LungVision™ system, a preoperative CT is loaded and the lesion is marked and contoured so the system knows the lesion size, shape and location before the procedure. During this step, the LungVision system derives the airways from the preoperative CT and can be a complete navigation bronchoscopy system for those looking to use it without a robotic or ENB system. If needed, a virtual bronchoscopy highlighting the preferred pathway to the lesion is provided. In this instance, the Ethicon MONARCH™ robotic bronchoscopy platform was used for navigation.
Registration
LungVision registration requires two C-arm spins – one around the main carina and another around the lesion. These two spins generate an initial C-Arm Based Computed Tomography (CABT) scan providing real-time lesion location.
Marking of the main carina on LungVision’s C-Arm Based Computed Tomography (CABT) during registration.
Marking of the lesion on LungVision’s CABT imaging during registration.
Marking of the lesion on LungVision’s AI Tomography during registration.
Navigation
The Ethicon MONARCH™ robot’s electromagnetic navigation (EMN) system was used for navigation.
Tool-in-Lesion Confirmation
Once at the target lesion location as shown by the Ethicon MONARCH™ robotic bronchoscopy platform, a biopsy needle was extended down the working channel of the bronchoscope and another C-arm spin was performed to better understand the spatial relationship between the tool and the lesion. The imaging acquired from this CABT spin confirmed that the tool was within the lesion.
LungVision C-Arm Based Tomography (CABT) imaging providing real-time confirmation of tool-in-lesion.
LungVision’s Any Tool 3D View also showed tool-in-lesion confirmation.
Biopsy and Dye Marking for Lobectomy
After obtaining tool-in-lesion confirmation, biopsy samples were acquired via biopsy needle with the help of LungVision’s real-time, augmented fluoroscopy.
LungVision’s augmented fluoroscopy showing real-time sampling via needle biopsy.
There was no ROSE on site but the Aquyre Biosciences CelTivity Biopsy System was used in the procedure to confirm malignant cells in the biopsy samples provided.
Image from Aquyre Biosciences CelTivity Biopsy System showing enlarged, pleomorphic cells, clumped in orientation and increased in luminescence. This is considered HIGH PROBABILITY for malignancy.
After confirming malignancy with CelTivity on the first pass, a fiducial coil dipped in indocyanine green (ICG) was placed at the lesion location using LungVision’s real-time augmented fluoroscopy to assist in evaluation for a Robotic Assisted Lobectomy. A segmentectomy was not possible due to the fact that the hilar lymph nodes were also involved.
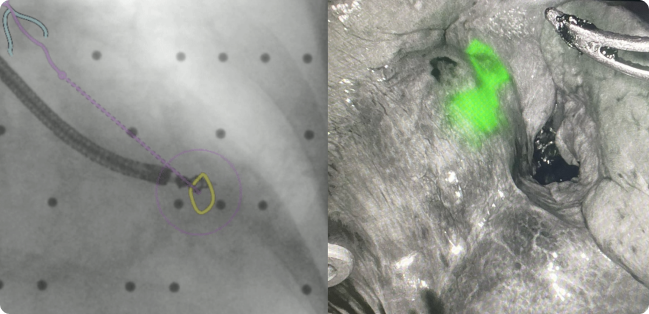
Under LungVision augmented fluoroscopy, fiducial coils dipped in were used to dye mark the lesion for immediate robotic-assisted lobectomy.
Image of lesion visualized under Firefly prior to lobectomy.
Final Pathology
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Conclusion
LungVision's AI-driven intraoperative CT imaging provided the real-time imaging required to confirm tool-in-lesion and accurately dye-mark the lesion for robotic-assisted lobectomy so that this patient could be definitively diagnosed, staged, and treated in one single-anesthesia event. This patient went home two days later.
About Dr. Tsai
Wilson Tsai, MD
Director, Thoracic Program
John Muir Health