Lesion Characteristics
Lesion Size (diameter): 12 mm (LUL) and 15 mm (RML)
Lesion Location: Left Upper Lobe (LUL) GGO and Right Middle Lobe (RML) Lesion
Visible on Fluoro: No
Case Information
Full Procedure Time: 60 Minutes
Final Pathology Report:
Lesion A: LUL: Chronic inflammation and fibrosis, negative for malignancy
Lesion B: RML: Chronic inflammation and fibrosis, negative for malignancy
Patient Background
A 65-year-old asymptomatic female, who has never smoked and has a history of multiple sclerosis (MS), underwent magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of her spine. The MRI incidentally revealed the presence of two lesions on computed tomography (CT), one located in the left upper lobe (LUL) and another in the right middle lobe (RML) of the lungs. Subsequently, the patient was referred to North Memorial Health Hospital for biopsies of both lesions and of her lymph nodes.
Preoperative CT showed the presence of two lesions.
PET also showed the presence of two lesions.
The Procedure
LungVision™ by Body Vision Medical was utilized as a standalone for both image-guided navigation and real-time, intraoperative imaging during the diagnostic bronchoscopy procedure.
Planning
During planning of the LungVision™ system, an initial preoperative CT scan is uploaded. The user marks and contours the lesion, providing the system with lesion size, shape, and pre-procedural location. Utilizing airway data derived from the preoperative CT scan, the LungVision™ system generates a virtual bronchoscopy (VB) which highlights the optimal pathway to the lesion.
Registration
Once the patient is on the table, LungVision™ registration consists of two rotations of the C-arm. The initial spin is isocentered around the main carina, and the subsequent is isocentered around the lesion. These two spins generate an initial C-Arm Based Tomography (CABT) scan showing the actual lesion location and thus eliminating CT-to-body divergence prior to navigation.
Registration of the main carina on LungVision™ system.
Lesion Registration on LungVision™ system.
Navigation to Lesion A
Guided by LungVision™ virtual bronchoscopy and real-time augmented fluoroscopy, navigation to the lesion was successfully performed. To enhance access to both of the lesions, a LungVision™ procedural kit, equipped with a pre-curved extended working channel, was utilized. The procedural kit’s catheter has a narrow diameter (OD of 2.6mm) to enable navigation further out into the periphery, a 90-degree pre-curved tip to more easily negotiate tight turns in the airways, and radiopaque markers to enable clear visualization of the catheter under fluoroscopy during navigation.
Navigation to lesion A under LungVision™ Augmented Fluoroscopy.
Biopsy and Fiducial Marking - Lesion A
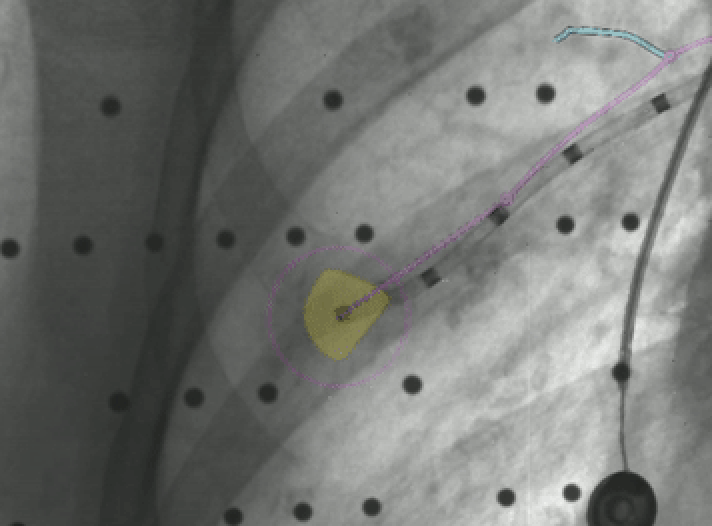
Once in close proximity to Lesion A, as confirmed by LungVision™ augmented fluoroscopy, a REBUS probe was inserted down the working channel and also returned a concentric signal, confirming the lesion location as indicated by LungVision™. Biopsy samples were acquired and a fiducial marker was placed in the lesion using LungVision™ augmented fluoroscopy to visually guide both procedures.
Biopsy of lesion A under LungVision™ Augmented Fluoroscopy.
Fiducial marker placement in Lesion A under LungVision™ Augmented Fluoroscopy
Navigation to Lesion B
Next, using LungVision™ virtual bronchoscopy and augmented fluoroscopy, navigation to lesion B was performed.
Navigation to lesion B under LungVision™ Augmented Fluoroscopy.
Tool-in-Lesion Confirmation, Biopsy, and Marking - Lesion 2
Another C-arm spin was performed to confirm tool-in-lesion with a LungVision™ CABT scan. In this case, REBUS returned an eccentric signal but the decision was made to proceed with tissue sampling. Biopsy samples were collected and a second fiducial marker was placed into the target via the extended working channel, again using LungVision™ augmented fluoroscopy for to visually guide both procedures.
LungVision™ tool-in-lesion confirmation showing “CABT” and “AI Tomo” views of Lesion B.
Tool-in-lesion of Lesion B confirmed with LungVision™3D View.
Biopsy of Lesion B under LungVision™ Augmented Fluoroscopy.
Fiducial marker placement in Lesion B under LungVision™ Augmented Fluoroscopy
Following biopsy of the second lesion, complete EBUS staging was performed.
Pathology
Lesion A: Chronic inflammation and fibrosis, negative for malignancy
Lesion B: Chronic inflammation and fibrosis, negative for malignancy
EBUS TBNA from stations 11R, 4R, 7, 4L, lymph nodes: Respiratory epithelium and lymphoid tissue with no pathologic abnormalities
Follow Up
Given the concerning findings on PET/blood tests, this patient was referred for bilateral CT-guided TTNAs performed on two separate dates in March 2023. These procedures confirmed the same diagnosis:
Lesion A: Lung tissue with nonspecific chronic inflammation. Negative for malignancy.
Lesion B: Lung tissue with nonspecific chronic inflammation and fibrosis. Negative for malignancy.
This patient will be monitored moving forward and is advised to stay up-to-date on all other cancer screening.
Conclusion
LungVision™ intraoperative CT imaging provided the AI-driven real-time imaging that enabled accurate navigation, visual tool-in-lesion confirmation, and image-guided biopsy of these 12 mm and 15 mm lesions. Subsequent TTNA procedures support the potential accuracy and specificity of the true negative diagnosis achieved with endobronchial biopsy using LungVision™ for navigation and real-time, intraoperative imaging.
About Dr. Stoy
Interventional Pulmonologist and Critical Care Physician
North Memorial Health Hospital
Minneapolis, MN